Walls are a foundational element in any structure, and understanding the right codes and standards is vital for effective wall construction, especially siding. Here’s a quick guide to help you navigate these standards:
General Wall Construction Requirements:
- Walls must resist wind pressures and wall-racking forces while providing weather protection
- A variety of wall sheathing products and systems are available to meet these needs.
Continuously Sheathed Wood Walls:
- This method handles uplift loads, lateral loads, and wind pressures efficiently.
- It connects to the roof and provides occupant protection, meeting International Residential Code (IRC) bracing requirements
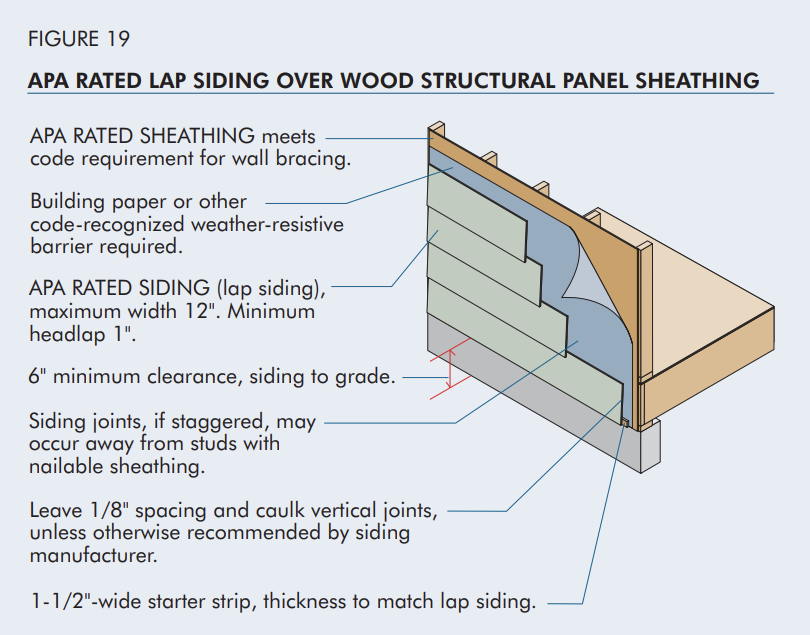
APA Panel Wall Sheathing:
- APA Rated Sheathing is versatile, used under siding or with insulated sheathing. It meets building code requirements for wall bracing, offering flexibility, especially for walls with windows and doors
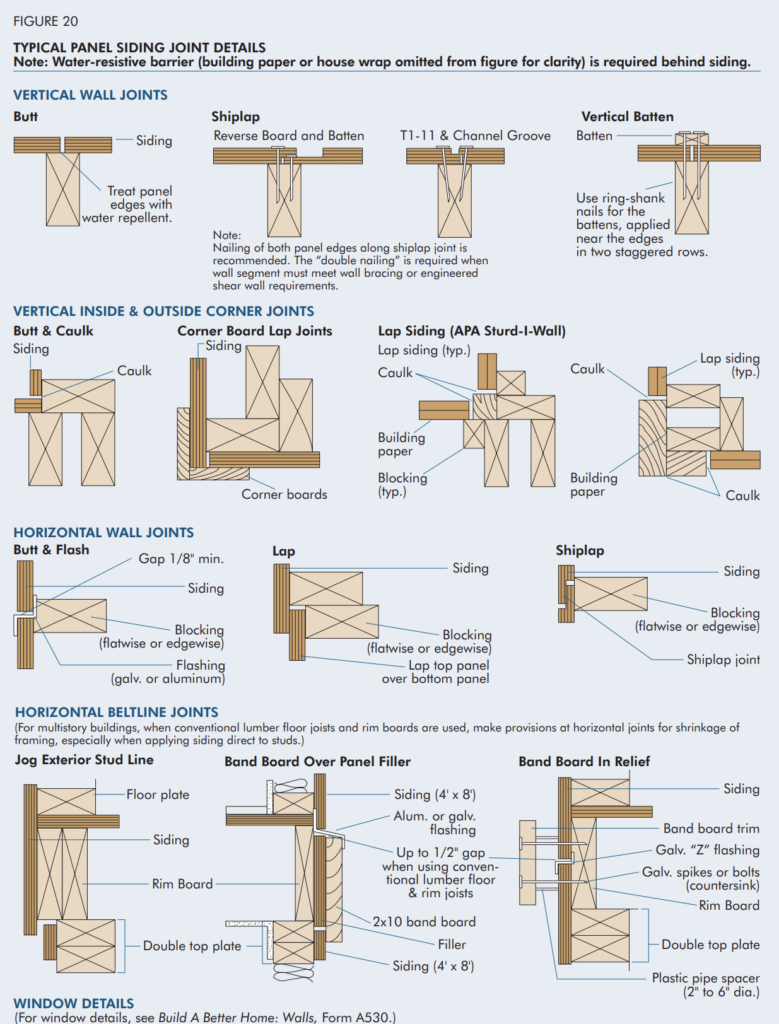
Wood Structural Panel Wall Bracing and Shear Walls:
- These are used to resist racking forces from wind or seismic events.
- Wall bracing is part of conventional construction as per 2018 International Building Code (IBC) Section 2308 and IRC Section 6.10
Sheathing as a Nail Base for Siding and Trim:
- Wood structural panel sheathing offers a strong base for various lightweight claddings like vinyl, wood, aluminum, fiber cement, and others.
- For claddings weighing 3 psf or less, using ring-shank nails is recommended to match the fastener spacing advised by the siding manufacturer
Considerations for Heavier Siding Products:
- Siding products heavier than 3 psf need special attention regarding fastening to sheathing.
- For detailed information on fastener types and their withdrawal resistance, APA’s Technical Topic TT-109 can be consulted
Siding Fasteners:
- Hot-dip galvanized nails are generally recommended for most siding applications.
- Stainless steel or aluminum nails can also be considered for enhanced performance. It’s important to finish the siding as per APA recommendations to prevent staining from galvanized fasteners
Siding Patterns and Grades
- APA Rated Siding: Includes 303 plywood siding, available in various surface textures and patterns.
- Variety: A wide range of surface patterns and thicknesses are available.
- Customization: For specific wood species characteristics, specify by grade and species preference.
- Reference: For detailed descriptions of siding surface patterns and thicknesses, refer to APA Product Guide: Performance Rated Siding Form E300
Siding Finishes
Care and Preparation
- Storage: Plywood should be stored in a cool, dry place, out of sunlight and weather.
- Handling: Handle with care to avoid damage before finishing.
- Edge Sealing: Edges and ends of APA Rated Siding panels or lap siding should be sealed to minimize moisture content changes.
- Factory vs. Site Sealing: Siding can be edge-sealed at the factory or on the job site. Cut edges during construction should be resealed
Finishing Options
- Finishing Products: APA Rated Siding can be finished with semi-transparent stains, solid-color stains, or paint systems.
- Types of Finishes:
- Semi-transparent Stains (Oil-based): Emphasize grain patterns, texture, and natural wood characteristics. Suitable for certain plywood face grades.
- Solid-Color Stains (Oil or All-acrylic Latex): Obscure color differences in the wood, providing a uniform appearance. Recommended for various grades, especially where semi-transparent stains are unsuitable.
- Paints (All-acrylic Latex): Recommended for all APA Rated Sidings (except brushed plywood). An all-acrylic latex paint system, with at least one stain-blocking prime coat and topcoat, is advised for best performance.
- Considerations: The choice of finish depends on the type of siding product and whether it has an overlaid surface. Consult manufacturer recommendations for specific products and finishes
For detailed installation guidelines and technical specifications, always refer to the latest building codes and manufacturer instructions. Remember, correct application not only ensures the structural integrity of your property but also enhances its aesthetic appeal and longevity.
For more personalized guidance, consult with engineers and local building codes specific to your location. For immediate service or consultation, you may contact us at Allied Emergency Services, INC.
Contact Information:
- Phone: 1-800-792-0212
- Email: Info@AlliedEmergencyServices.com
- Location: Serving Illinois, Wisconsin, and Indiana with a focus on the greater Chicago area.
If you require immediate assistance or have specific questions, our human support is readily available to help you.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only. For professional advice, consult experts in the field
![How Much Does a New Roof Cost in Illinois? [2024 Pricing Guide]](https://www.news.alliedemergencyservices.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/DALL·E-2024-05-07-15.14.25-A-professional-roofing-contractor-inspecting-a-roof-in-the-foreground-of-a-picturesque-suburban-neighborhood-in-Illinois.-The-contractor-is-wearing-a--150x150.webp)









