Introduction: The APA – The Engineered Wood Association established the Performance Standards and Qualification Policy for Structural-Use Panels in the 1980s, aiming to standardize wood-based structural panels. This initiative includes specific guidelines for Rated Sturd-I-Floor, Rated Sheathing, and Rated Siding, ensuring quality and consistency in construction materials.
Key Standards and Qualifications:
Historical Context: The APA developed these standards in the early 1980s, adding performance criteria for Rated Siding in 1984. An agreement with NIST in 1991 led to a national standard, harmonizing U.S. and Canadian requirements under the Product Standard PS 2, finalized in 1992
Rated Sturd-I-Floor and Sheathing: These panels are used as subfloors and underlayments, with particular emphasis on cross-panel strength and racking shear properties. They’re also employed in construction for roofing, subflooring, and wall sheathing
Rated Siding: This category is intended for exterior siding applications, emphasizing performance dimensions, tolerances, and moisture content. It includes wood-based structural-use panels and lap siding
Raw Materials and Panel Construction: The policy stipulates strict requirements for wood veneer and other materials used in panel manufacture. Panels are classified into all-veneer, composite, or mat-formed types, each meeting specific construction and performance criteria
Performance Testing: Panels undergo rigorous testing for various structural conditions like static and impact loads, stability, and fastener head pull-through. These tests ensure compliance with established performance criteria
Physical and Surface Characteristics: Panels are evaluated for stability, edge swell, surface texture changes, and finish adhesion. These characteristics are crucial for the long-term durability and appearance of the panels
Bond Performance: This includes the adhesive bonding system, with specific requirements for veneer, mat-formed panels, and composite panels. The standards require a minimum average strength retention, with tests conducted following specific moisture cycling procedures
Dimensional Tolerance and Moisture Content: The policy sets tolerances for panel size, thickness, squareness, and straightness, ensuring uniformity in manufactured panels. The moisture content at the time of shipment is also regulated
Identification and Trademarking: All siding panels must bear the APA trademark, indicating compliance with the standards. This mark includes information about the panel’s thickness, bond performance, and span rating. Manufacturers must also adhere to APA’s application recommendations and provide any additional guidelines.
General Reference to ASTM Methods
ASTM E661 (Concentrated Static and Impact Tests): This method is used for testing concentrated static loads and impact loads. The procedures involve variations like using a steel test frame and adjusting the weight of the shot bag based on span ratings
ASTM D3043 (Quality Assurance Bending Test): This method develops bending strength and stiffness information for quality assurance purposes, following the principles of ASTM D3043 Method D for specimen preparation and test procedure
ASTM E72 (Wall Performance Under Racking Loads): The general provisions of Sections 14 and 15 of ASTM E72 are followed for testing wall performance under racking loads
ASTM D1761 and D1037 (Nail Holding Tests): These tests measure the resistance to nail withdrawal and nail head pull-through in panels, adhering to the latest editions of ASTM D1761 Section 10.2 and ASTM D1037 Section 15
ASTM D3043 Method C (Small Specimen Bending for Quality Assurance): This method tests for stiffness and maximum bending moment along and across the panel strength axis, in line with ASTM D3043 Method C
ASTM D3501 Method B (Panel Compression Test): This procedure provides data on compression properties of panel products, following the general procedures of ASTM D3501 Method B
ASTM D1037 (Linear Expansion Measured by Exposure to Relative Humidity): This method measures linear expansion as per ASTM D1037 Sections 108 to 111, particularly for variations in moisture content
ASTM E661 (Siding Performance Under Soft-Body Impact Loads): Used for determining the performance of siding products under soft-body impact loads, such as impacts from a person running or falling against a wall
ASTM D3043 (Linear Expansion and Thickness Swell Test): This method provides a quick evaluation of a panel’s dimensional stability, aligning with specifications in ASTM D3043
APA Test Methods
APA Test Method D-2: Mold Test
APA Test Method D-3: Bacteria Test
APA Test Method D-4: Moisture Cycle for OSB Qualification (Single Cycle Test)
APA Test Method D-5: Moisture Cycle For Delamination And Strength Retention (Six-Cycle Test)
APA Test Method D-7: Moisture Cycle for Quality Assurance Bending Test General
APA Test Method S-1: Sheathing And Sturd-I-Floor Performance Under Concentrated Static And Impact Loads
APA Test Method S-2: Sheathing And Sturd-I-Floor Performance Under Uniform Loads
APA Test Method S-3: Wall Performance Under Racking Loads
APA Test Method S-4: Fastener-Holding Performance
APA Test Method S-5: Panel Bending
APA Test Method S-6: Small Specimen Bending For Quality Assurance
APA Test Method S-9: Siding Performance Under Concentrated Static Loads
APA Test Method S-10: Siding Performance Under Uniform Loads
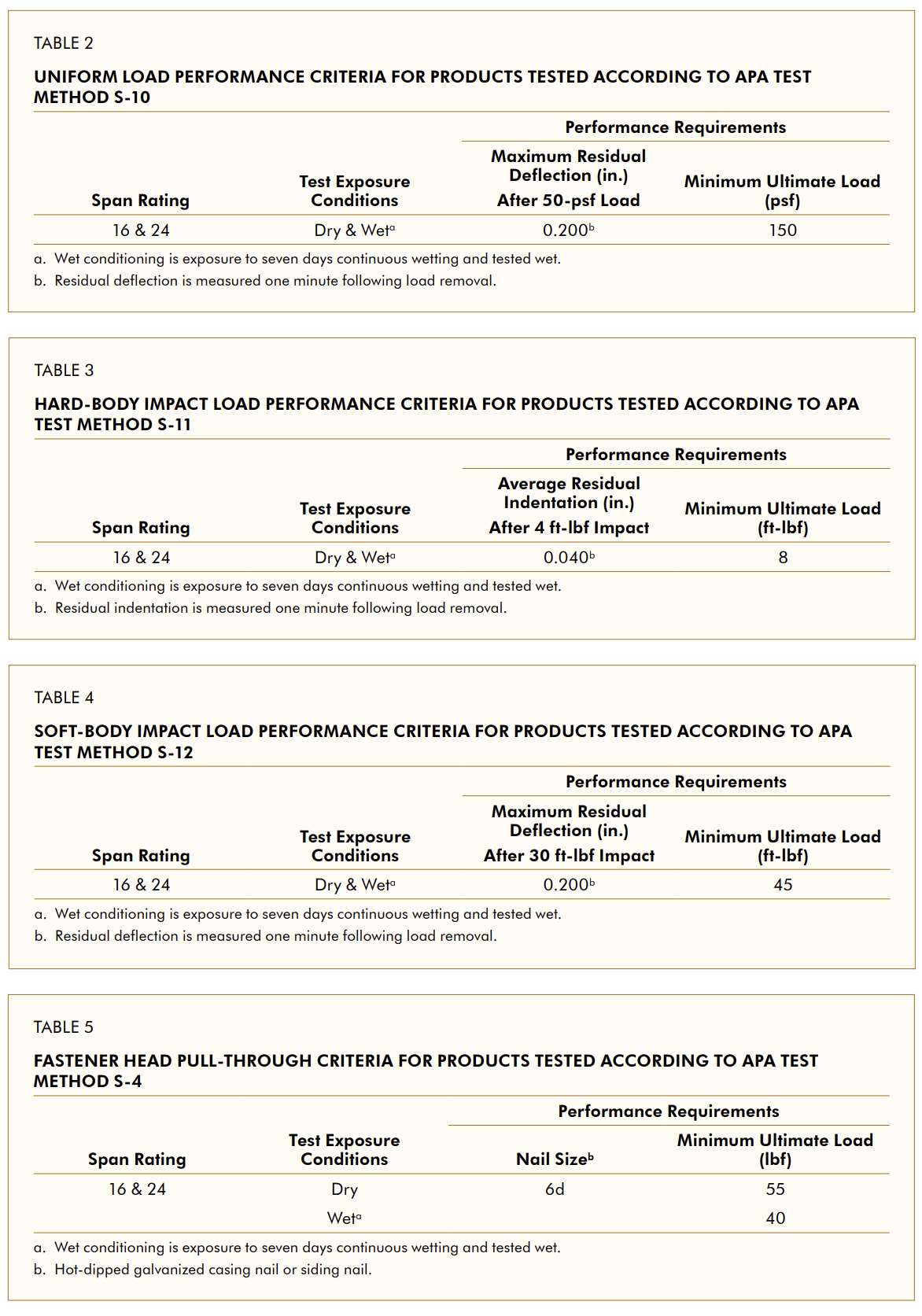
APA Test Method S-11: Siding Performance Under Hard-Body Impact Loads
APA Test Method S-12: Siding Performance Under Soft-Body Impact Loads
APA Test Method S-13: Panel Compression
APA Test Method S-14: Quality Assurance Bending Test
APA Test Method P-1: Linear Expansion And Thickness Swell Measured From Oven Dry or 50% Relative Humidity to Vacuum-Pressure Soak
APA Test Method P-2: Linear Expansion Measured After Wetting On One Side
APA Test Method P-3: Linear Expansion Measured by Exposure to Relative Humidity
APA Test Method P-4: Linear Expansion Measured In A Full‑Scale Frame
APA Test Method P-6: Panel Moisture Content
APA Test Method P-7: Panel Thickness
APA Test Method P-8: Panel Density
APA Test Method P-9: Probe Test For Delamination
APA Test Method P-10: Panel Stability Coefficient For Siding
APA Test Method P-11: Buckling Performance Measured On A Large-Scale Wall
APA Test Method P-12: Probe Test For Edge Checking Of Siding
APA Test Method F-1: Surface Change Measured After Soak‑Dry Cycles
APA Test Method F-2: Finish Adhesion on Wood-Based Siding
APA Test Method F-3: Surface Repair Performance In Wood-Based Siding
APA Test Method F-4: Overlay Performance On Wood-Based Siding
Conclusion: The Performance Standards and Qualification Policy for Wood Structural Panels by APA plays a pivotal role in ensuring the quality and reliability of wood-based structural panels in the construction industry. These comprehensive standards and rigorous testing protocols help maintain consistency and safety in building materials, benefiting both the construction sector and end-users.
For more personalized guidance, consult with engineers and local building codes specific to your location. For immediate service or consultation, you may contact us at Allied Emergency Services, INC.
Contact Information:
- Phone: 1-800-792-0212
- Email: Info@AlliedEmergencyServices.com
- Location: Serving Illinois, Wisconsin, and Indiana with a focus on the greater Chicago area.
If you require immediate assistance or have specific questions, our human support is readily available to help you.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only. For professional advice, consult experts in the field