Introduction
For homes located in regions prone to high winds, hurricanes, and seismic activity, the structural integrity of roofs and their extensions such as dormers and skylights is critical. This guide will focus on best practices and materials relevant to new construction to ensure maximum resistance against these natural forces.
Metal Structural Connectors: The Backbone of Resistance
Traditional methods of joining framing members like toe nailing are no longer sufficient for homes in high-risk areas. Metal structural connectors—straps, ties, screws—have become essential for enhancing structural integrity. These connectors are especially crucial for dormers, which face extreme forces during storms.
Key Considerations:
- Use connectors that are suitable for the specific load and direction of force.
- Metal connectors must be installed according to manufacturer’s or engineer’s specifications.
- The geographic location of the construction site will determine the level of corrosive weather exposure for the connector.
Relevant Resources:
Roof and Wall Bracing: Strengthening the Structure
The use of engineered trusses for roofing is increasingly popular. Proper bracing during installation is essential for these trusses to function effectively. Wall bracing is critical for preventing shear wall failure during high winds and seismic events.
Key Considerations:
- Trusses should be braced at the top and web cord with diagonal bracing.
- Wall bracing methods depend on the local codes and the building’s shape and size.
- For dormers, ensure that the walls are sufficiently braced to resist high wind speeds.
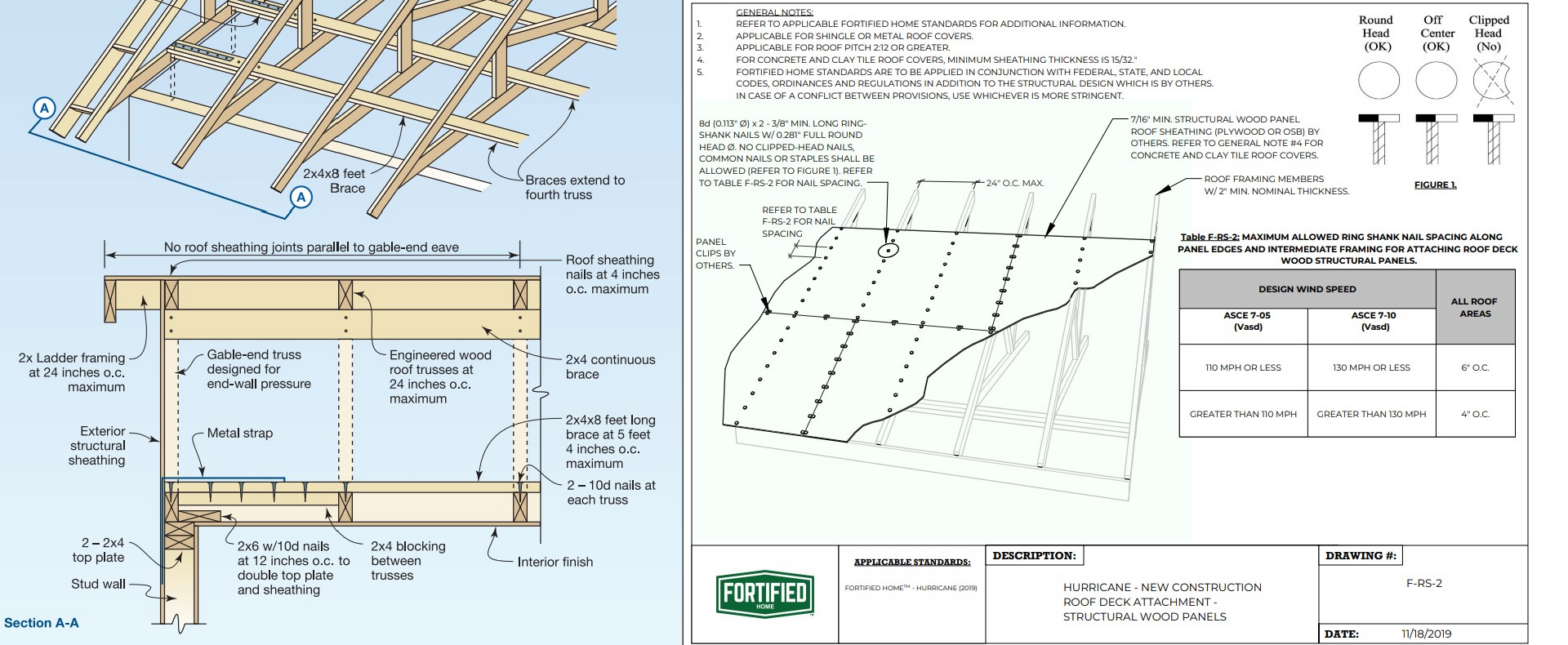
Secure Roof Sheathing: The First Line of Defense
The roof sheathing is critical for transferring uplift forces from roofing materials to the structural elements. In high-wind regions, thicker sheathing panels, tighter fastener spacing, and ring shank nails are recommended.
Key Considerations:
- Adhere to generic building code specifications for high wind regions found in ICC 2014, Chapter 7, Roof Assemblies.
Impact-Rated Skylights and Windows: Protecting the Building Envelope
Impact-resistant glazing systems are essential for protecting the building envelope from high-velocity projectiles during storms.
Key Considerations:
- Use laminated glass or polycarbonate glazing systems.
- Compliance with ASTM E1996 and ASTM E1886 is essential for impact-resisting standards.
How to Design and Specify Roof Connections
A meticulous preconstruction design and specification process is crucial for building roofs capable of withstanding extreme forces. This includes load path analysis, adequate bracing, and correct metal connector usage.
How to Construct a Dormer in High Wind and Hurricane Regions
- Frame the Roof Opening: Use engineering design specifications and local building codes for guidance.
- Wall Connections: Use metal straps to connect dormer walls to the main roof.
- Roof-to-Wall Connections: Use hurricane ties or other suitable metal connectors.
- Secure the Roof Sheathing: Use adhesives, metal clips, and a dense nailing pattern.
- Install Impact-Rated Skylights and Windows: Ensure they meet local building codes and engineering specifications.
International Residential Code (IRC) Compliance
- Table 301.2(2): Component and Cladding Loads for wind resistance.
- Table R802.11: Rafter or Truss Uplift Connection Forces from Wind.
- Fastener Requirements: Specifics on nail or screw size, length, and spacing for wind and seismic resistance.
- Seismic Resistance: Guidelines based on seismic design categories A through E.
Florida Building Code Compliance
- Wind Zones: Buildings must be built to withstand up to 180 MPH winds in the strictest zones.
- Wall Sheathing: Minimum of 5/8-inch thickness.
- Window Glazing Impact Testing: Must meet TAS 201, TAS 202, and TAS 203 or ASTM E1886 and ASTM E1996 standards.
IBHS FORTIFIED Home Compliance
- FORTIFIED Roof: Specific nail spacing and type for roof decking.
- Tiered Certifications: Roof, Silver, and Gold levels for whole-house certifications.
Metal Connector and Fastener Manufacturer’s Manuals
- Fit for Purpose: Documentation must be available to prove the suitability of steel structural connectors.
- Nail Specifications: Color-coded or size-stamped for post-installation verification.
Conclusion
Adhering to the best practices and guidelines mentioned above can significantly enhance the structural integrity of your home’s roof and its extensions, offering maximum resistance against high winds, hurricanes, and seismic activity.
For more personalized guidance, consult with engineers and local building codes specific to your location. For immediate service or consultation, you may contact us at Allied Emergency Services, INC.
Contact Information:
- Phone: 1-800-792-0212
- Email: Info@AlliedEmergencyServices.com
- Location: Serving Illinois, Wisconsin, and Indiana with a focus on the greater Chicago area.
If you require immediate assistance or have specific questions, our human support is readily available to help you.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only. For professional advice, consult experts in the field