In the realm of home improvements, few upgrades offer the immediate benefits and long-term savings like high-performance windows. These technological marvels not only enhance your home’s comfort but also contribute to significant energy savings. Let’s delve into what makes these windows high-performance and why they’re a must-have for any modern home.
Technical Description:
- Efficiency Levels: High-performance windows, often labeled as ENERGY STAR certified, boast efficiency levels surpassing standard windows by at least 15%. Some even achieve ultra-efficiency, exceeding 50% improvement.
- Innovative Features: These windows integrate advanced technologies such as multiple glass panes separated by insulating spacers, inert gases like argon or krypton for enhanced thermal resistance, and low-emissivity coatings to regulate heat transfer and block harmful UV rays.
- Alternate Terms: They go by various names like Enhanced Comfort Windows, Quiet Windows, or Advanced Window Technology, emphasizing their superior performance.
Benefits:
- Year-Round Comfort: High-performance windows effectively regulate indoor temperature, keeping your home cooler in summer and warmer in winter, ensuring year-round comfort.
- Energy Savings: By minimizing heat loss and gain, these windows significantly reduce energy consumption, translating to lower utility bills and a reduced carbon footprint.
- Noise Reduction: Enhanced insulation properties not only keep unwanted heat out but also dampen external noise, providing a quieter and more peaceful indoor environment.
Scope:
- Selecting and Installing: When choosing windows, prioritize ENERGY STAR rated options or those exceeding ENERGY STAR requirements. Consider triple-pane windows for maximum efficiency.
Description:
- Utility Savings: Installing ENERGY STAR-rated windows can save homeowners 7% to 15% on utility bills while enhancing thermal comfort, according to ENERGY STAR estimates.
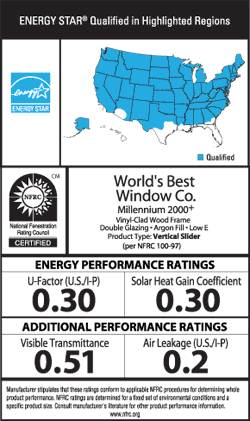
- Technical Specifications: ENERGY STAR windows typically feature two or three panes with insulating frames and coatings to improve efficiency. The NFRC label provides performance ratings across key metrics like U-Factor, SHGC, and Air Leakage.
How to Purchase and Install ENERGY STAR windows
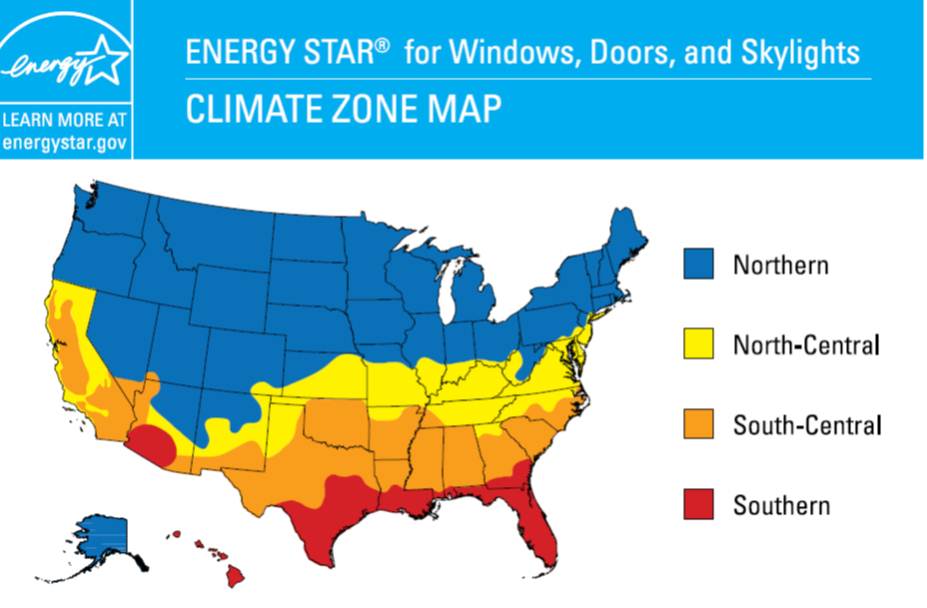
- Determine Your ENERGY STAR Climate Zone: Use the ENERGY STAR climate zone finder tool, which bases the climate zone on the county in which your home is located.
- Look for ENERGY STAR-Labeled Products: Seek out ENERGY STAR-labeled products that meet or exceed the criteria for your climate zone. When ordering from a showroom or building materials supplier, ensure you ask for a product that meets the ENERGY STAR criteria in your specific climate zone. In colder climates, consider exploring the opportunity to use Most Efficient products for enhanced energy efficiency.
- Consider Program Criteria: If you intend to have your home certified under programs like the DOE Zero Energy Ready Home program or the ENERGY STAR Single-Family New Homes program, refer to the Compliance tab for additional window specifications required to meet those program criteria.
- Check for Rebates and Incentives: Check with local utilities and visit the ENERGY STAR website to learn about federal tax credits for ENERGY STAR-rated windows and other utility rebate programs. Some utilities offer significant rebates for selecting Most Efficient products. Additionally, explore the DOE Database of State Incentives for Renewables & Efficiency for information on additional state, federal, and local tax credits and exemptions.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Installation Instructions: When installing the windows, make sure to follow the manufacturer’s installation instructions meticulously to avoid voiding the warranty. Some warranties may even require the use of an installer certified by the manufacturer.
- Properly Seal Windows: Ensure proper installation to keep air and moisture out. Refer to guides like “Fully Flashed Window and Door Openings” and “Air Sealing Window and Door Rough Openings” for detailed instructions on how to properly air seal around window rough openings.
Ensuring Success:
- Optimization: Push the envelope by selecting the most efficient windows, especially in regions with high heating loads.
- Climate Considerations: Design your window placement and features to maximize solar heat gain in colder climates and minimize it in hotter regions.
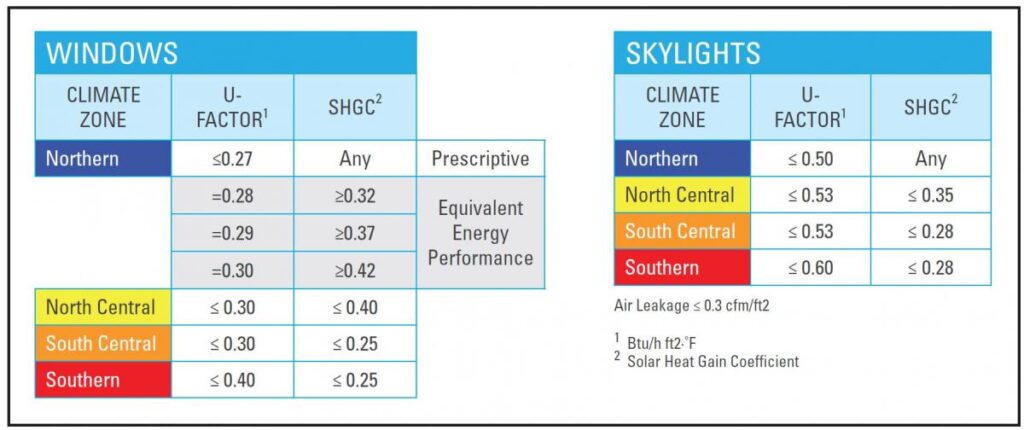
Compliance Requirements for High-Performance Windows
- ENERGY STAR Single-Family New Homes, Version 3/3.1:
- The ENERGY STAR Reference Design Home outlines efficiency features, including fenestration (windows) requirements.
- Requirements are detailed in Exhibit 1 of the National Program Requirements document.
- DOE Zero Energy Ready Home (Revision 07):
- Fenestration must meet or exceed ENERGY STAR window requirements as specified in Exhibit 1’s mandatory requirements.
- 2009-2021 IECC and IRC Window U-Factor Requirements Table:
- Specifies maximum U-Factor and Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) requirements for fenestration (windows) and skylights in new homes.
- 2009 International Energy Conservation Code (IECC):
- Section 303.1.3 Fenestration Product Rating:
- U-Factors of fenestration products (windows, doors, and skylights) must be determined per NFRC 100 and labeled and certified by the manufacturer.
- Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) must be determined per NFRC 200 and labeled and certified by the manufacturer.
- Products without labels will be assigned default U-Factor and SHGC values as specified in Table 303.1.3(1) and Table 303.1.3(3) respectively.
- Table 402.1.1 Insulation and Fenestration Requirements:
- Lists insulation and fenestration requirements by building component.
- Section 402.3.1 U-Factor:
- An area-weighted average is permitted to meet U-Factor requirements.
- Section 402.3.2 Glazed Fenestration SHGC:
- An area-weighted average of products with more than 50 percent glazing can meet SHGC requirements.
- Section 402.3.3 Glazed Fenestration Exemption:
- Up to 15 square feet per dwelling unit may be exempted from U-Factor and SHGC requirements under the prescriptive approach.
- Section 402.3.4 Opaque Door Exemption:
- One side-hinged door up to 24 square feet may be exempted from the U-Factor requirement.
- Section 303.1.3 Fenestration Product Rating:
- 2012, 2015, and 2018 IECC:
- Similar requirements as 2009 IECC with additional updates.
- Compliance sections include R303.1.3 and R402.3.1-4.
- Compliance measures include area-weighted averages for U-factor and exemptions for certain glazed fenestration.
- 2009 International Residential Code (IRC):
- Table N1102.1.1 Insulation and Fenestration Requirements by Component.
- Section N1101.5 Fenestration Product Rating:
- U-Factors of fenestration products (windows, doors, and skylights) must be determined per NFRC 100 and labeled and certified by the manufacturer.
- Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) must be determined per NFRC 200 and labeled and certified by the manufacturer.
- Products without labels must meet the requirements specified in Table N1101.5(1) – Table N1101.5(3).
- Section N1102.3.1 U-Factor:
- An area-weighted average is permitted to satisfy the U-factor requirements.
- Section N1102.3.2 Glazed Fenestration SHGC:
- An area-weighted average of products with more than 50 percent glazing can satisfy the SHGC requirements.
- Section N1102.3.3 Glazed Fenestration Exemption:
- Up to 15 square feet per dwelling unit may be exempted from U-factor and SHGC requirements under the prescriptive approach.
- Section N1102.3.4 Opaque Door Exemption:
- One side-hinged door up to 24 square feet may be exempted from the U-factor requirement.
- 2012 International Residential Code (IRC):
- Section N1101.12.3 Fenestration Product Rating:
- U-Factors of fenestration products (windows, doors, and skylights) must be determined per NFRC 100 and labeled and certified by the manufacturer.
- Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) and visible transmittance must be determined per NFRC 200 and labeled and certified by the manufacturer.
- Products without labels must meet the requirements specified in Table N1101.12.3(1) – N1101.12.3(3).
- Section N1102.3.1 U-Factor:
- An area-weighted average is allowed to satisfy the U-factor requirements.
- Section N1102.3.2 Glazed Fenestration SHGC:
- An area-weighted average of products with more than 50 percent glazing is allowed to satisfy the SHGC requirements.
- Section N1102.3.3 Glazed Fenestration Exemption:
- Up to 15 square feet per dwelling unit may be exempted from U-factor and SHGC requirements under the prescriptive approach.
- Section N1102.3.4 Opaque Door Exemption:
- One side-hinged door up to 24 square feet may be exempted from the U-factor requirement.
- Section N1101.12.3 Fenestration Product Rating:
- 2015 and 2018 International Residential Code (IRC):
- Section N1101.10.3 Fenestration Product Rating:
- U-Factors of fenestration products (windows, doors, and skylights) are determined by an accredited independent laboratory per NFRC 100 and labeled and certified by the manufacturer.
- Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) and visible transmittance are determined by an accredited independent laboratory per NFRC 200 and labeled and certified by the manufacturer.
- Products without labels must meet the requirements specified in Table N1101.12.3(1) – N1101.12.3(3).
- Section N1102.1.2 (R402.1.2) Insulation and Fenestration Criteria:
- Insulation and fenestration criteria are listed in Table N1102.1.2 by climate zone.
- Section N1102.3.1 U-Factor:
- An area-weighted average is allowed to satisfy the U-factor requirements.
- Section N1102.3.2 Glazed Fenestration SHGC:
- An area-weighted average of products with more than 50 percent glazing is allowed to satisfy the SHGC requirements.
- Section N1102.3.3 Glazed Fenestration Exemption:
- Up to 15 square feet per dwelling unit may be exempted from U-factor and SHGC requirements under the prescriptive approach.
- Section N1102.3.4 Opaque Door Exemption:
- One side-hinged door up to 24 square feet may be exempted from the U-factor requirement.
- Section N1101.10.3 Fenestration Product Rating:
- Retrofit Requirements:
- Retrofit projects must adhere to respective energy codes and standards based on construction year and jurisdiction.
- Details provided in Retrofit sections for IECC and IRC.
- Appendix J (IRC):
- Regulates repair, renovation, alteration, and reconstruction of existing buildings.
- Intended to ensure continued safe use of existing structures.
Certifications: Ensure compliance with relevant programs like ENERGY STAR Single-Family New Homes or the DOE Zero Energy Ready Home program.
Code Requirements: Familiarize yourself with fenestration requirements outlined in the International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) or the International Residential Code (IRC) for your region.
High-performance windows aren’t just a luxury; they’re a smart investment for any homeowner looking to enhance comfort, save on energy costs, and reduce environmental impact. With their advanced features and tangible benefits, these windows are a cornerstone of modern, sustainable living.
For immediate service or consultation, you may contact us at Allied Emergency Services, INC.
Contact Information:
- Phone: 1-800-792-0212
- Email: Info@AlliedEmergencyServices.com
- Location: Serving Illinois, Wisconsin, and Indiana with a focus on the greater Chicago area.
If you require immediate assistance or have specific questions, our human support is readily available to help you.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only. For professional advice, consult experts in the field.