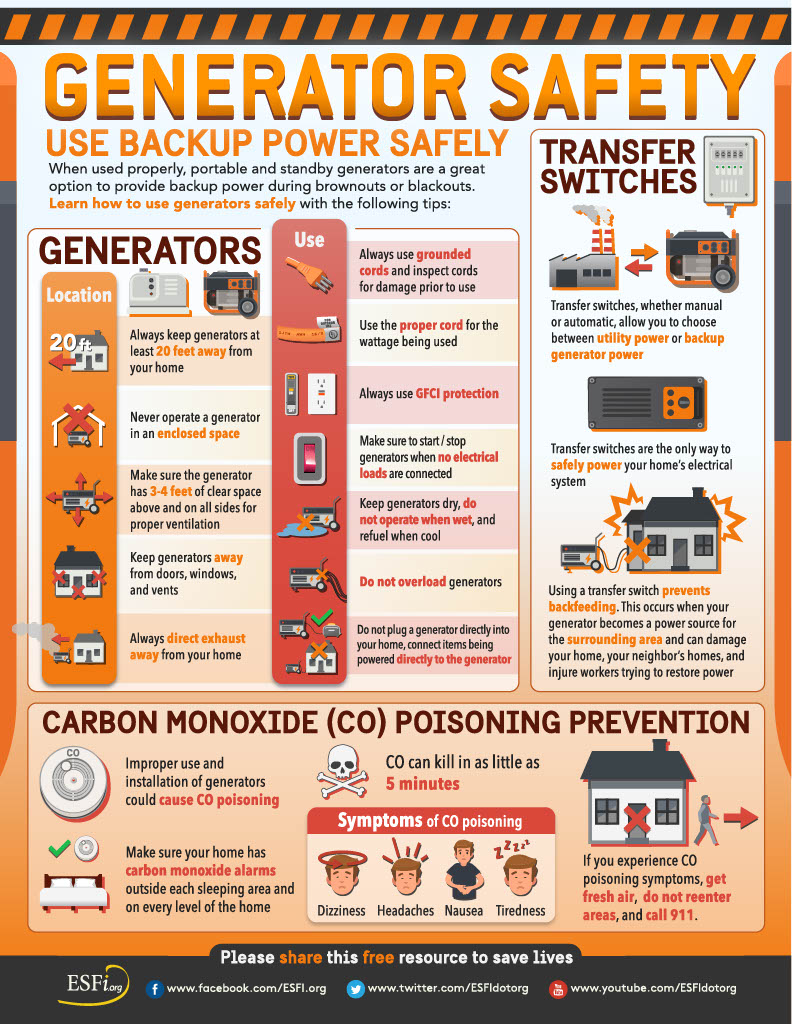
Power outages can be frustrating and disruptive, especially during severe weather events or grid disruptions. That’s why more households are turning to generators as a reliable source of backup power. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the use of generators for backup power and how to do it safely and effectively.
Why Use Generators for Backup Power?
Severe weather events and grid disruptions are becoming increasingly common, and having a backup power source can provide essential electricity for critical needs such as heating, cooling, refrigeration, cooking, medical equipment, water pumps, and more.
Types of Generators
Generators come in various types, and choosing the right one depends on your specific needs and circumstances:
- Portable Generators: These smaller consumer-type generators are portable and run on gasoline or propane. They are suitable for temporary use to power essential circuits.
- Permanent Generators: Larger permanently installed units are ideal for whole-house backup power. They can run on natural gas, gasoline, diesel, or liquid propane and are commonly used in rural areas or places prone to frequent power outages.
- Battery/Inverter Units: Portable, rechargeable battery/inverter units are pre-charged using grid power and can also be recharged using solar panels or other renewable sources. They provide a clean and quiet backup power solution.
- Household Battery Backup/Inverter Systems: These systems store power from the grid or renewable sources, such as rooftop solar panels or wind turbines, for use during outages. They offer a sustainable backup power solution.
- Industrial and Commercial Generators: For larger power needs, industrial and commercial generators with engines greater than 50 bhp or 37 kW are available, running on diesel, gasoline, propane, or natural gas.
Safety First
Operating generators safely is crucial to prevent accidents and carbon monoxide poisoning. Here are some safety tips:
- Outdoor Operation: Never operate a generator inside your home, garage, or basement. It should be placed outdoors at least twenty feet away from your home and protected from snow and rain.
- Ventilation: Ensure that the generator exhaust faces away from your house to prevent the buildup of carbon monoxide inside. Install carbon monoxide detectors in your home for added safety.
- Fuel Storage: Store fuel for the generator safely outside in quantities appropriate for your needs. Consider using fuel stabilizers to prevent spoilage over time.
- Professional Installation: Engage a licensed electrician to install a transfer switch that prevents backfeeding. This switch allows you to choose between utility power and generator power and ensures safety.
Connecting the Generator
There are several ways to connect a generator to your home’s electrical system:
- Manual Transfer Switch: Installed adjacent to the electrical panel, this switch connects key circuits, such as the furnace, water pump, refrigerator, and select lights and receptacles, to the generator.
- Interlock: This setup in the electric panel allows you to control which circuits are powered by the generator. It’s a flexible option for choosing critical circuits during an outage.
- Socket-Mounted Transfer Switch: Shaped like a cylinder, this switch fits between the meter and the meter base on the exterior of your house. A cable from the generator plugs into an outlet on this cylinder.
It’s important to check with local electrical authorities before installing any generator connection method to ensure compliance.
Generator Selection
Selecting the right generator depends on your specific needs and circumstances. Consider factors like home ownership, plans for renewable energy sources, budget, and desired power capacity when choosing a generator.
Generator Installation
Proper installation of a generator is essential for safety and functionality. Here are some installation considerations:
- Site Selection: Choose a location for the generator and fuel storage tank that minimizes flood risk and provides easy access for fuel delivery.
- Elevation: In areas with high snow loads or seasonal flooding, elevate the generator platform and pad to prevent damage.
- Shelter: Construct a shelter with a roof and vented sides to protect the generator from snow and rain.
- Safety Measures: Keep the generator and fuel tank at least 20 feet away from your home, and install safety features to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Electrician’s Expertise: Engage a licensed electrical contractor to design, permit, and install the generator circuitry, transfer switch, and necessary wiring upgrades.
Using generators for backup power during power outages can provide peace of mind and essential electricity for your household’s needs. By following safety guidelines and considering your specific requirements, you can choose the right generator and ensure it’s installed correctly for reliable backup power.
For immediate service or consultation, you may contact us at Allied Emergency Services, INC.
Contact Information:
- Phone: 1-800-792-0212
- Email: Info@AlliedEmergencyServices.com
- Location: Serving Illinois, Wisconsin, and Indiana with a focus on the greater Chicago area.
If you require immediate assistance or have specific questions, our human support is readily available to help you.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only. For professional advice, consult experts in the field.