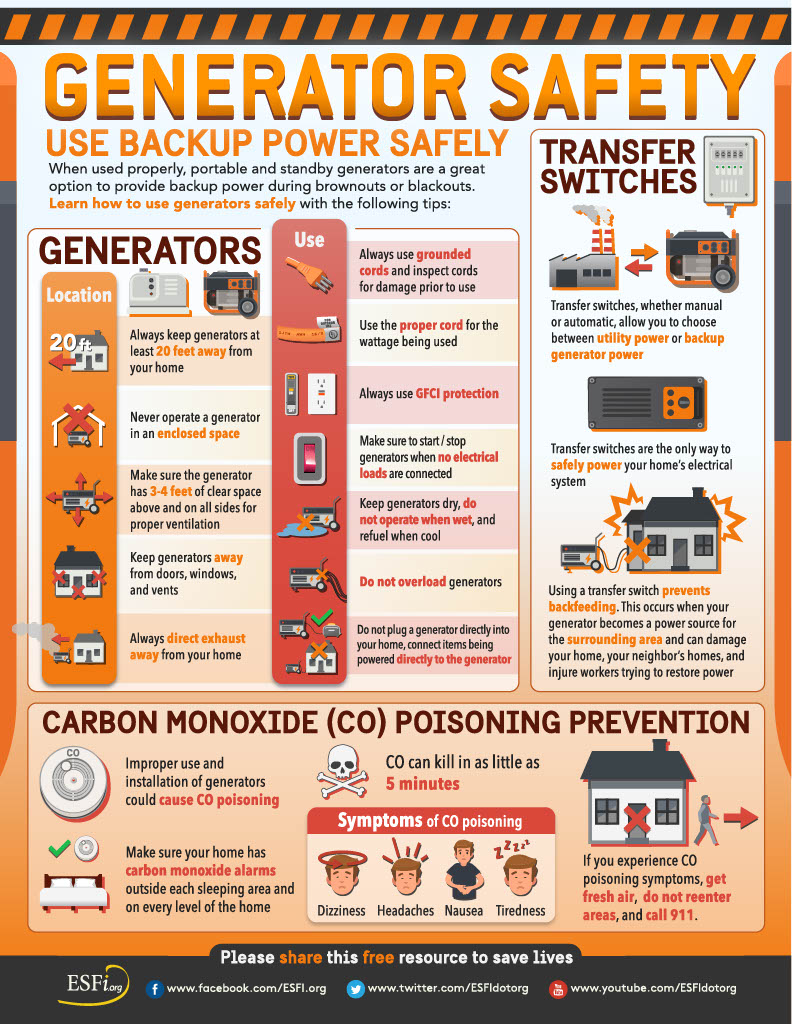
Portable generators play a crucial role in providing temporary or remote power, especially during emergencies and disasters. These internal combustion engines are essential tools, but their safe use is paramount. One critical aspect of using portable generators safely is understanding the grounding requirements. In this guide, we will explore the grounding requirements for portable generators and essential safety practices to prevent shocks, electrocutions, and injuries.
When Grounding is Not Required:
- Portable generators do not need to be grounded if they meet specific conditions:
- The generator supplies only equipment mounted on the generator and/or cord-and-plug-connected equipment through receptacles on the generator (OSHA 1926.404(f)(3)(i)(A)).
- The noncurrent-carrying metal parts of the generator equipment, such as the fuel tank, internal combustion engine, and housing, are bonded to the generator frame (OSHA 1926.404(f)(3)(i)(B)).
- In such cases, the generator’s frame serves as the ground instead of connecting to a grounding electrode system.
When Grounding is Required:
- If the portable generator is providing electric power to a structure (home, office, shop, trailer, etc.) through a transfer switch, it must be connected to a grounding electrode system like a driven ground rod.
- The transfer switch should be approved for use and installed by a qualified electrician following the manufacturer’s instructions.
Major Causes of Injuries and Fatalities:
- Shocks and electrocutions can occur due to improper use of portable generators.
- Utility workers can face shocks and electrocutions if the generator is improperly connected to structures like residences, offices, shops, or trailers.
Safe Work Practices:
- Always maintain and operate portable generators according to the manufacturer’s use and safety instructions.
- Never attach a portable generator directly to the electrical system of a structure unless it has a properly installed open-transition transfer switch.
- Plug electrical appliances and tools directly into the generator using manufacturer-supplied cords, and use heavy-duty extension cords with grounding conductors.
- Proper grounding and bonding are essential to prevent shocks and electrocutions.
- Utilize ground-fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) as per the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Do not connect a generator to a structure unless it has a properly installed transfer switch.
- Visually inspect equipment before use, remove defective items from service, and label them as unsafe for use.
Verification by Testing:
- It’s important to confirm the integrity of the connection between the generator’s frame and the equipment grounding terminals of power receptacles through testing by a competent electrician.
- The ohmic resistance should measure near zero and must not be intermittent, indicating a loose connection.
Bonding Versus Grounding:
- Bonding and grounding are separate requirements for generators. Grounding connects the generator’s circuit or equipment to reference ground (including the generator’s frame), while bonding is the connection between the grounded circuit conductor (neutral) and the generator’s frame.
- Proper bonding of the neutral conductor to the generator’s frame is crucial for safe use, and it can be confirmed through testing by a competent electrician.
For more information, refer to OSHA’s guidelines (DSTM 10/2005).
This information helps ensure the safe use of portable generators and prevents potential electrical hazards.
Ensuring the proper grounding of portable generators is vital for the safety of users and utility workers. By adhering to the grounding requirements and following safe work practices, we can significantly reduce the risks associated with portable generator use. Remember, safety should always be the top priority when working with these essential power sources. Stay informed, follow guidelines, and use portable generators responsibly to protect yourself and others from potential electrical hazards.
For immediate service or consultation, you may contact us at Allied Emergency Services, INC.
Contact Information:
- Phone: 1-800-792-0212
- Email: Info@AlliedEmergencyServices.com
- Location: Serving Illinois, Wisconsin, and Indiana with a focus on the greater Chicago area.
If you require immediate assistance or have specific questions, our human support is readily available to help you.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only. For professional advice, consult experts in the field.
![How Much Does a New Roof Cost in Illinois? [2024 Pricing Guide]](https://www.news.alliedemergencyservices.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/DALL·E-2024-05-07-15.14.25-A-professional-roofing-contractor-inspecting-a-roof-in-the-foreground-of-a-picturesque-suburban-neighborhood-in-Illinois.-The-contractor-is-wearing-a--150x150.webp)